When a user receives an inquiry that "the server cannot be accessed", the solution is different between the case where the server can be operated directly and when it is necessary to operate it remotely.Eventually, the server will be operated directly, but first of all, let's explain from a case where it cannot be operated directly, such as a server at another base.
Remote survey
If you have to respond to a server at another base, or if you have to respond in an urgent business trip or at home, you have to investigate the server status.At that time, the first report from the user is an important source of information.In order to understand the situation in detail and accurate situation, you must be able to contact the reporter as needed.However, from the perspective of the administrator, it is important to note that the user is an amateur, so it does not necessarily always report information accurately.
Remote troubles are basically the procedure shown in Fig. 1.First, let's try from the classic ping command.Of course, it is a prerequisite that the firewall settings will not refuse ping.
Figure 1 Basic procedure for trouble shooting with remote
If you can solve your name with DNS (Domain Name System), try ping with the host name.If there is a response at the IP address and an error is caused by the host name, there is a problem with DNS (screen 1).
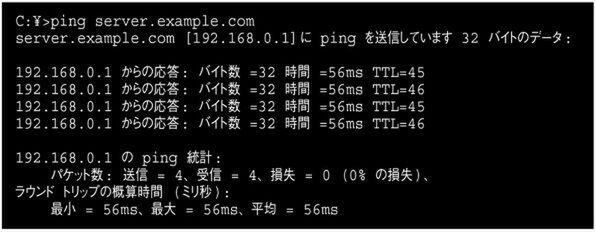
Try to ping with the host name, checking if the name can be resolved on the screen 1 DNS
However, it is not possible to judge that the server is down immediately just because the error is caused by ping.If there is a router on the way, there may be a problem with the router and may not be able to access the server.Just in case, try the Tracert command (for Windows) (screen 2).The Tracert command uses ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) to check the router's response to the target server, like ping.
In the case of screen 2 Windows, "Tracert" is omitted so that it fits within 8 characters, but in the case of Linux, it becomes "Traceroute" with full spell.
If there is no problem with ping or the like, depending on the server, you can check if the service is down in a simple way using Telnet.
For example, if you are an email server, access port numbers 25 (SMTP) and 110 (POP) to see if the service is available (screen 3).If you enter the command directly, and if there is no normal response from the server, you can judge that the service is down.Let's try remotely login on the server on Telnet or SSH again to find out the operating status of the service.If you can't log in, you may be in a serious situation.
Screen 3 Telnet usage examples
Remote surveys are separated so far.For more details, investigate the server directly locally.
(The next page, "Investigate the server directly -first from the power supply ~")


